Spring Security源碼解析之權(quán)限訪問控制是如何做到的
在實戰(zhàn)篇《話說Spring Security權(quán)限管理(源碼詳解)》我們學(xué)習(xí)了Spring Security強大的訪問控制能力,只需要進行寥寥幾行的配置就能做到權(quán)限的控制,本篇來看看它到底是如何做到的。
一、再聊過濾器鏈源碼篇中反復(fù)提到,請求進來需要經(jīng)過的是一堆過濾器形成的過濾器鏈,走完過濾器鏈未拋出異常則可以繼續(xù)訪問后臺接口資源,而最后一個過濾器就是來判斷請求是否有權(quán)限繼續(xù)訪問后臺資源,如果沒有則會將拒絕訪問的異常往上向異常過濾器拋,異常過濾器會對異常進行翻譯,然后響應(yīng)給客戶端。
所以,一般情況下最后一個過濾器是做權(quán)限訪問控制的核心過濾器FilterSecurityInterceptor ,而倒數(shù)第二個是異常翻譯過濾器ExceptionTranslationFilter ,將異常進行翻譯然后響應(yīng)給客戶端。比如我們實戰(zhàn)項目過濾器鏈圖解
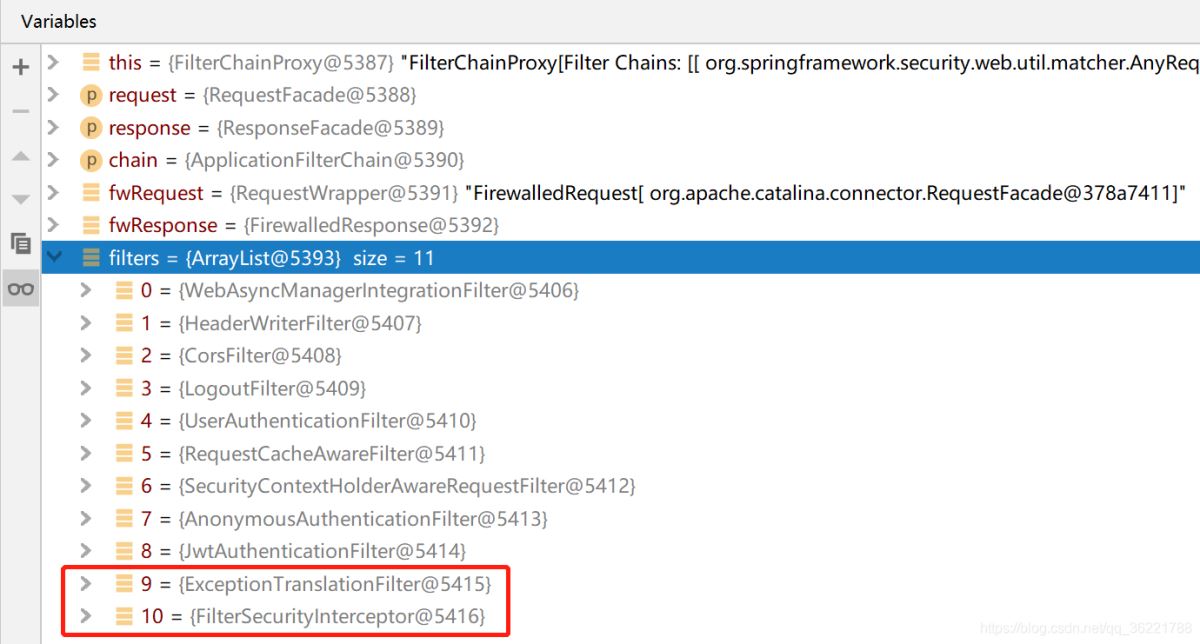
這個過濾器的配置器是 ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer ,它的父類 AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer 中的 configure() 方法創(chuàng)建了這個過濾器。
abstract class AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer<C extends AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer<C, H>, H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>>extends AbstractHttpConfigurer<C, H> {...@Overridepublic void configure(H http) throws Exception {FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource metadataSource = createMetadataSource(http);if (metadataSource == null) {return;}FilterSecurityInterceptor securityInterceptor = createFilterSecurityInterceptor(http, metadataSource, http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));if (filterSecurityInterceptorOncePerRequest != null) {securityInterceptor.setObserveOncePerRequest(filterSecurityInterceptorOncePerRequest);}securityInterceptor = postProcess(securityInterceptor);http.addFilter(securityInterceptor);http.setSharedObject(FilterSecurityInterceptor.class, securityInterceptor);}...}
這個過濾器的配置器是在 HttpSecurity 的 authorizeRequests() 方法中apply進來的,在我們自己配置的核心配置器中使用的就是該種基于 HttpServletRequest 限制訪問的方式。
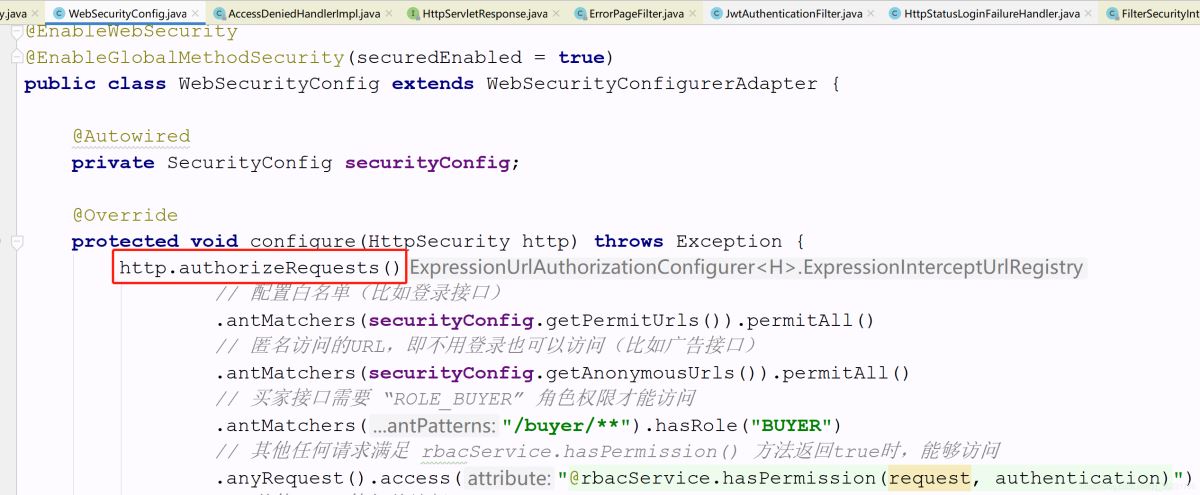
這個過濾器的配置器是 ExceptionHandlingConfigurer ,它自己的 configure() 方法中創(chuàng)建了這個過濾器。
public final class ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>> extendsAbstractHttpConfigurer<ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<H>, H> {...@Overridepublic void configure(H http) throws Exception {AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);ExceptionTranslationFilter exceptionTranslationFilter = new ExceptionTranslationFilter(entryPoint, getRequestCache(http));if (accessDeniedHandler != null) {exceptionTranslationFilter.setAccessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);}exceptionTranslationFilter = postProcess(exceptionTranslationFilter);http.addFilter(exceptionTranslationFilter);}...}
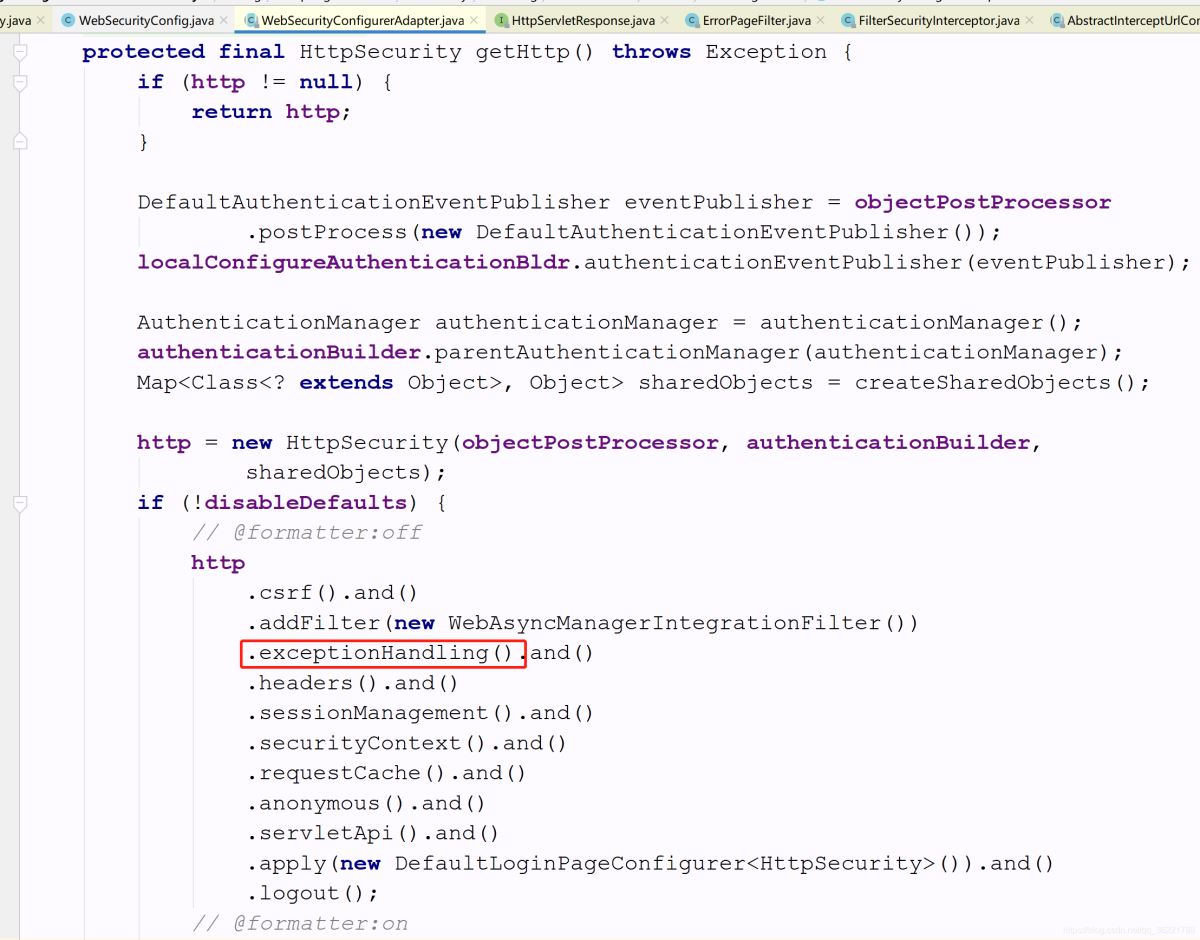
這個過濾器的配置器是在 HttpSecurity 的 exceptionHandling() 方法中apply進來的,和上面不同的是,這個過濾器配置器會默認(rèn)被apply進 HttpSecurity,在 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 中的 init() 方法,里面調(diào)用了 getHttp() 方法,這里定義了很多默認(rèn)的過濾器配置,其中就包括當(dāng)前過濾器配置。
這個方法里面有個 attributes ,里面獲取的就是當(dāng)前request請求所能匹配中的權(quán)限Spel表達式,比如這里是 hasRole(’ROLE_BUYER’)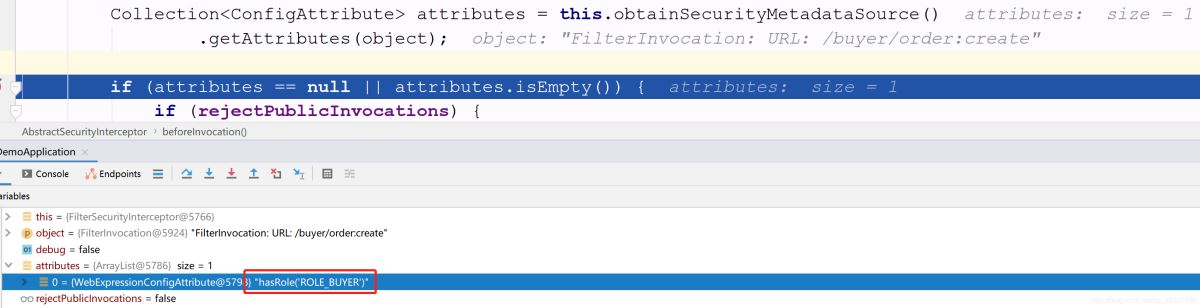 方法源碼如下,繼續(xù)往下走
方法源碼如下,繼續(xù)往下走
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {...// 獲取當(dāng)前request請求所能匹配中的權(quán)限Spel表達式Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);...// Attempt authorizationtry {this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);}catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,accessDeniedException));throw accessDeniedException;}...}
進入:decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes)
這里有個投票器,投票結(jié)果為1表示可以訪問直接返回,投票結(jié)果為-1表示拒絕訪問,向上拋拒絕訪問異常,這里使用的投票器是 WebExpressionVoter
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {int deny = 0;for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug('Voter: ' + voter + ', returned: ' + result);}switch (result) {case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:return;case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:deny++;break;default:break;}}if (deny > 0) {throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage('AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied', 'Access is denied'));}// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstainedcheckAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();}
進入:vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes)
這里面其實就是使用Spring的Spel表達式進行投票,使用請求中的權(quán)限表達式組裝Expression,使用Token令牌中的權(quán)限組裝EvaluationContext,然后調(diào)用 ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx),
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi,Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {assert authentication != null;assert fi != null;assert attributes != null;WebExpressionConfigAttribute weca = findConfigAttribute(attributes);if (weca == null) {return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;}EvaluationContext ctx = expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication,fi);ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);return ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx) ? ACCESS_GRANTED: ACCESS_DENIED;}
evaluateAsBoolean() 方法里面就是調(diào)用Expression的 getValue() 方法,獲取實際的匹配結(jié)果,如下圖Spel表達式為 hasRole(’ROLE_BUYER’)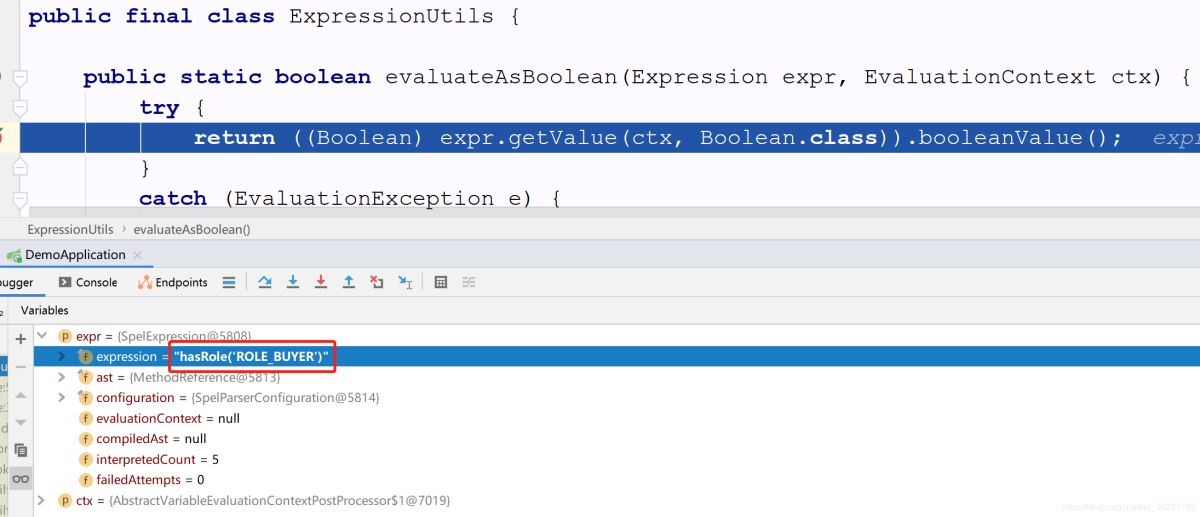 所以它實際調(diào)用的是 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasRole 方法(關(guān)于權(quán)限表達式對應(yīng)實際調(diào)用的方法,在《手把手教你如何使用Spring Security(下):訪問控制》文章中已貼出,下面文章也補充一份),里面的邏輯其實就是判斷Token令牌中是否包含有 ROLE_BUYER 的角色,有的話返回true,否則返回false,如下為 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasRole 方法源碼:
所以它實際調(diào)用的是 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasRole 方法(關(guān)于權(quán)限表達式對應(yīng)實際調(diào)用的方法,在《手把手教你如何使用Spring Security(下):訪問控制》文章中已貼出,下面文章也補充一份),里面的邏輯其實就是判斷Token令牌中是否包含有 ROLE_BUYER 的角色,有的話返回true,否則返回false,如下為 SecurityExpressionRoot#hasRole 方法源碼:
private boolean hasAnyAuthorityName(String prefix, String... roles) {Set<String> roleSet = getAuthoritySet();for (String role : roles) {String defaultedRole = getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(prefix, role);if (roleSet.contains(defaultedRole)) {return true;}}return false;} 如果投票成功,則會一直返回到 invoke() 方法,再執(zhí)行后續(xù)過濾器,未拋異常表示該請求已經(jīng)有訪問權(quán)限了 假如投票失敗,在 decide() 方法中會向上拋拒絕訪問異常,一直往上拋直到被處理,往上反向跟蹤發(fā)現(xiàn)這個過濾器一直沒有處理拒絕訪問異常,那就繼續(xù)往上個過濾器拋,就到了我們的異常翻譯過濾器 ExceptionTranslationFilter。ExceptionTranslationFilter
該過濾器的 doFilter() 方法很簡單,沒有邏輯處理,只對后續(xù)過濾器拋出的異常進行處理,源碼如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)throws IOException, ServletException {HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;try {chain.doFilter(request, response);logger.debug('Chain processed normally');}catch (IOException ex) {throw ex;}catch (Exception ex) {// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktraceThrowable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);if (ase == null) {ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);}if (ase != null) {handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);}else {// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-isif (ex instanceof ServletException) {throw (ServletException) ex;}else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {throw (RuntimeException) ex;}// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn’t actually happen// as we’ve already covered all the possibilities for doFilterthrow new RuntimeException(ex);}}}
當(dāng)拋出拒絕訪問異常后,繼續(xù)調(diào)用 handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception) 方法,方法里面主要將異常信息和錯誤碼設(shè)置到響應(yīng)頭,然后響應(yīng)到客戶端,請求結(jié)束。
補充:權(quán)限表達式
權(quán)限表達式(ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer) 說明 Spel表達式 Spel表達式實際執(zhí)行方法(SecurityExpressionOperations) permitAll() 表示允許所有,永遠返回true permitAll permitAll() denyAll() 表示拒絕所有,永遠返回false denyAll denyAll() anonymous() 當(dāng)前用戶是anonymous時返回true anonymous isAnonymous() rememberMe() 當(dāng)前用戶是rememberMe用戶時返回true rememberMe isRememberMe() authenticated() 當(dāng)前用戶不是anonymous時返回true authenticated isAuthenticated() fullyAuthenticated() 當(dāng)前用戶既不是anonymous也不是rememberMe用戶時返回true fullyAuthenticated isFullyAuthenticated() hasRole(“BUYER”) 用戶擁有指定權(quán)限時返回true hasRole(‘ROLE_BUYER’) hasRole(String role) hasAnyRole(“BUYER”,“SELLER”) 用于擁有任意一個角色權(quán)限時返回true hasAnyRole (‘ROLE_BUYER’,‘ROLE_BUYER’) hasAnyRole(String… roles) hasAuthority(“BUYER”) 同hasRole hasAuthority(‘ROLE_BUYER’) hasAuthority(String role) hasAnyAuthority(“BUYER”,“SELLER”) 同hasAnyRole hasAnyAuthority (‘ROLE_BUYER’,‘ROLE_BUYER’) hasAnyAuthority(String… authorities) hasIpAddress(‘192.168.1.0/24’) 請求發(fā)送的Ip匹配時返回true hasIpAddress(‘192.168.1.0/24’) hasIpAddress(String ipAddress),該方法在WebSecurityExpressionRoot類中 access('@rbacService.hasPermission(request, authentication)') 可以自定義Spel表達式 @rbacService.hasPermission (request, authentication) hasPermission(request, authentication) ,該方法在自定義的RbacServiceImpl類中 四、總結(jié) 訪問控制的核心過濾器是 FilterSecurityInterceptor ,當(dāng)然這個是可選的,我們完全也可以自定義一個過濾器去處理權(quán)限訪問。 處理訪問異常處理的過濾器是 ExceptionTranslationFilter ,里面邏輯很簡單,給response設(shè)置異常信息錯誤碼,再返回給客戶端。以上就是Spring Security源碼解析之權(quán)限訪問控制是如何做到的的詳細內(nèi)容,更多關(guān)于Spring Security權(quán)限訪問控制的資料請關(guān)注好吧啦網(wǎng)其它相關(guān)文章!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 利用單元測試對PHP代碼進行檢查2. python如何實現(xiàn)word批量轉(zhuǎn)HTML3. Java8內(nèi)存模型PermGen Metaspace實例解析4. python excel和yaml文件的讀取封裝5. python3實現(xiàn)往mysql中插入datetime類型的數(shù)據(jù)6. moment轉(zhuǎn)化時間戳出現(xiàn)Invalid Date的問題及解決7. python爬蟲實戰(zhàn)之制作屬于自己的一個IP代理模塊8. Django 權(quán)限管理(permissions)與用戶組(group)詳解9. App啟動優(yōu)化-Android性能優(yōu)化10. 詳解docker pull 下來的鏡像都存到了哪里
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備