Android+OpenCv4實(shí)現(xiàn)邊緣檢測(cè)及輪廓繪制出圖像最大邊緣
基于Canny算法的邊緣檢測(cè)主要有5個(gè)步驟,依次是高斯濾波、像素梯度計(jì)算、非極大值像素梯度抑制、滯后閾值處理和孤立弱邊緣抑制。Canny在有噪聲的情況下表現(xiàn)好不好,取決于前面的降噪過程,可以手動(dòng)做高斯處理提高識(shí)別率。
/**image 輸入圖像,必須是CV_8U的單通道或者三通道圖像。edges 輸出圖像,與輸入圖像具有相同尺寸的單通道圖像,且數(shù)據(jù)類型為CV_8U。threshold1 第一個(gè)滯后閾值。threshold2 第二個(gè)滯后閾值。apertureSize Sobel算子的直徑。L2gradient 計(jì)算圖像梯度幅值方法的標(biāo)志。默認(rèn)為false**/public static void Canny(Mat image, Mat edges, double threshold1, double threshold2, int apertureSize, boolean L2gradient)
使用
/** * canny算法,邊緣檢測(cè) */ public static Mat canny(Bitmap bitmap) {Mat mSource = new Mat();Utils.bitmapToMat(bitmap, mSource);Mat grayMat = new Mat();Imgproc.cvtColor(mSource,grayMat,Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);//轉(zhuǎn)換成灰度圖Mat mat = mSource.clone();Imgproc.Canny(mSource, mat, 75, 200);return mat; }

/** * 返回邊緣檢測(cè)之后的最大矩形,并返回 * * @param cannyMat * Canny之后的mat矩陣 * @return */ public Rect findMaxRect(Mat cannyMat) {Mat tmp = mSource.clone();List<MatOfPoint> contours = new ArrayList<MatOfPoint>();Mat hierarchy = new Mat();// 尋找輪廓Imgproc.findContours(cannyMat, contours, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);int index = 0;double perimeter = 0;// 找出匹配到的最大輪廓for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) { // 最大面積// double area = Imgproc.contourArea(contours.get(i)); //最大周長(zhǎng) MatOfPoint2f source = new MatOfPoint2f(); source.fromList(contours.get(i).toList()); double length = Imgproc.arcLength(source,true); if(length>perimeter){perimeter = length;index = i; }} /** * 參數(shù)一:image,待繪制輪廓的圖像。 * * 參數(shù)二:contours,待繪制的輪廓集合。 * * 參數(shù)三:contourIdx,要繪制的輪廓在contours中的索引,若為負(fù)數(shù),表示繪制全部輪廓。 * * 參數(shù)四:color,繪制輪廓的顏色。 * * 參數(shù)五:thickness,繪制輪廓的線條粗細(xì)。若為負(fù)數(shù),那么繪制輪廓的內(nèi)部。 * * 參數(shù)六:lineType,線條類型。FILLED LINE_4 4連通 LINE_8 8連通 LINE_AA 抗鋸齒 */Imgproc.drawContours(tmp,contours,index,new Scalar(0.0, 0.0, 255.0),9,Imgproc.LINE_AA);Rect rect = Imgproc.boundingRect(contours.get(index));//Imgproc.rectangle(tmp, rect, new Scalar(0.0, 0.0, 255.0), 4, Imgproc.LINE_8);showImg(tmp);return rect; } /** * 顯示圖像 * @param mat */ private void showImg(Mat mat){Bitmap bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mat.width(), mat.height(), Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);Utils.matToBitmap(mat, bitmap);mIvSrc.setImageBitmap(bitmap);mat.release(); }
最終效果圖
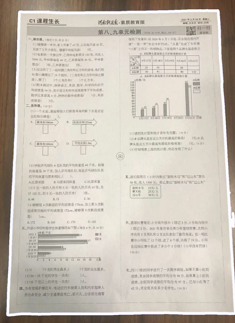
獲得矩形坐標(biāo)點(diǎn)以后,后期可以做裁剪,旋轉(zhuǎn)之類操作,可以自行研究。
到此這篇關(guān)于Android+OpenCv4實(shí)現(xiàn)邊緣檢測(cè)及輪廓繪制出圖像最大邊緣的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Android OpenCv4邊緣檢測(cè)內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. moment轉(zhuǎn)化時(shí)間戳出現(xiàn)Invalid Date的問題及解決2. python爬蟲實(shí)戰(zhàn)之制作屬于自己的一個(gè)IP代理模塊3. 為什么你的android代碼寫得這么亂4. Java剖析工具YourKit 發(fā)布5.0版本5. 跟我學(xué)XSL(一)第1/5頁(yè)6. 使用JSP技術(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的在線測(cè)試系統(tǒng)的實(shí)例詳解7. Python中內(nèi)建模塊collections如何使用8. 動(dòng)態(tài)設(shè)置django的model field的默認(rèn)值操作步驟9. 開發(fā)效率翻倍的Web API使用技巧10. Docker創(chuàng)建本地鏡像實(shí)現(xiàn)方法解析
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備