你肯定能看懂的Java IO相關(guān)知識總結(jié)
操作系統(tǒng)就是管家,電腦的設備就是資源,如果進程先要操作資源,必須要進行系統(tǒng)調(diào)用,有操作系統(tǒng)去處理,然后再返回給進程,這樣的代理模式是不是很常見?因此app 就是你寫的程序,資源就是硬盤或者其他的設備,io就是進行的系統(tǒng)調(diào)用。
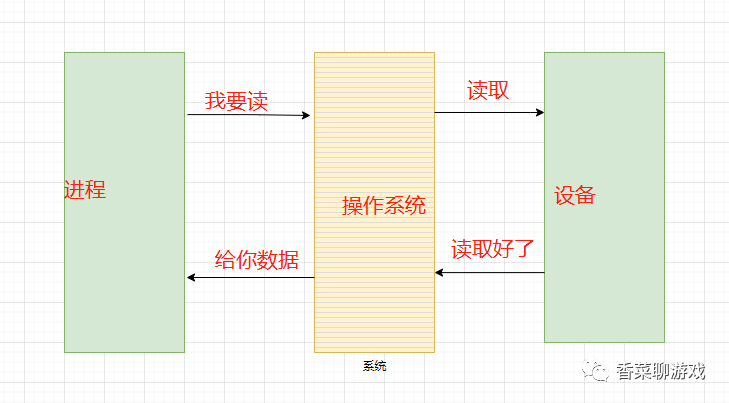
為了保證操作系統(tǒng)的穩(wěn)定性和安全性,一個進程的地址空間劃分為 用戶空間(User space) 和 內(nèi)核空間(Kernel space ) 。像我們平常運行的應用程序都是運行在用戶空間,只有內(nèi)核空間才能進行系統(tǒng)態(tài)級別的資源有關(guān)的操作,比如如文件管理、進程通信、內(nèi)存管理等等。也就是說,我們想要進行 IO 操作,一定是要依賴內(nèi)核空間的能力。并且,用戶空間的程序不能直接訪問內(nèi)核空間。當想要執(zhí)行 IO 操作時,由于沒有執(zhí)行這些操作的權(quán)限,只能發(fā)起系統(tǒng)調(diào)用請求操作系統(tǒng)幫忙完成。因此,用戶進程想要執(zhí)行 IO 操作的話,必須通過 系統(tǒng)調(diào)用 來間接訪問內(nèi)核空間
二、梳理類的結(jié)構(gòu)java的io 實在太復雜了,往往新手很難掌握,因為只緣身在此山中,新手往往很難從全體去看到問題的本質(zhì),我和打鐵的朋友的聊天截圖能幫你解答一些。

類結(jié)構(gòu)如下
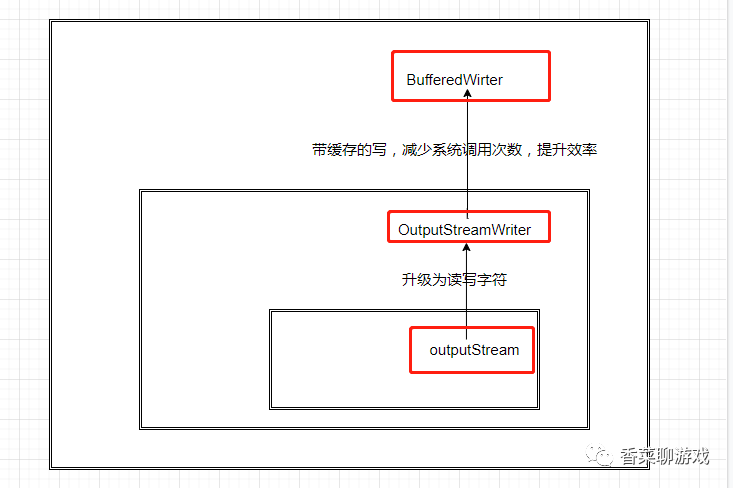
在平常的讀寫文件的時候可以先用基本流,然后看是否需要字符流,最后在用上帶buffer 的流。
IO流的設計思想就是裝飾器模式,一層一層的進行升級功能。
三、IO類大點兵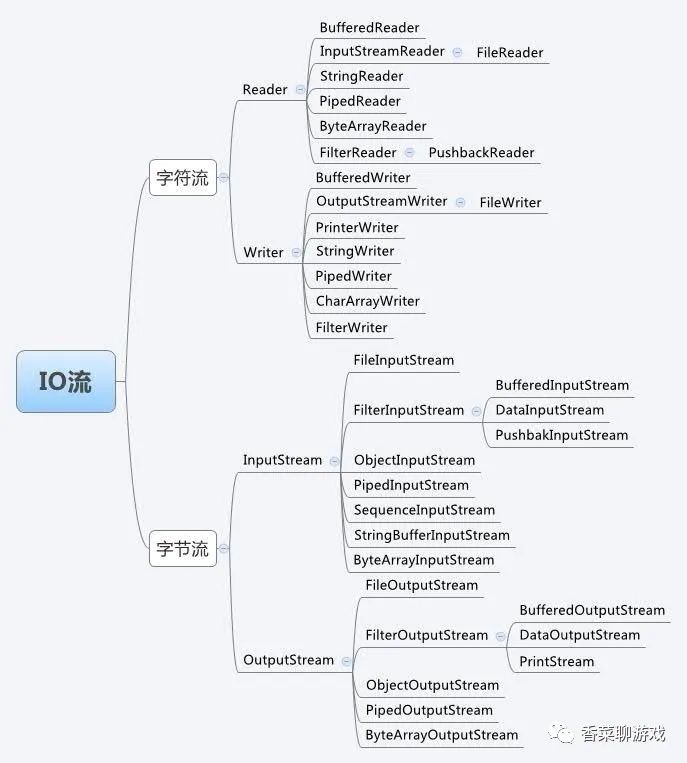
1、訪問操作文件(FileInputStream/FileReader ,F(xiàn)ileOutputStream/FileWriter)
import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException; /*** 拷貝文件* @author 香菜*/public class CopyFileWithStream { public static void main(String[] args) { int b = 0; String inFilePath = 'D:wechatA.txt'; String outFilePath = 'D:wechatB.txt'; try (FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(inFilePath); FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream(outFilePath)) { while ((b = in.read()) != -1) { out.write(b); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println('文件復制完成'); }}
2、緩存流的使用(BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream,BufferedReader/BufferedWriter)
package org.pdool.iodoc; import java.io.*; /*** 拷貝文件** @author 香菜*/public class CopyFileWithBuffer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String inFilePath = 'D:wechatA.txt'; String outFilePath = 'D:wechatB.txt'; try (BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(inFilePath)); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(outFilePath))) { byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int off = 0; while ((off = bis.read(b)) > 0) { bos.write(b, 0, off); } } }}
3、獲取鍵盤輸入
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestScanner { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNextLine()){ System.out.println(scanner.nextLine()); } }}
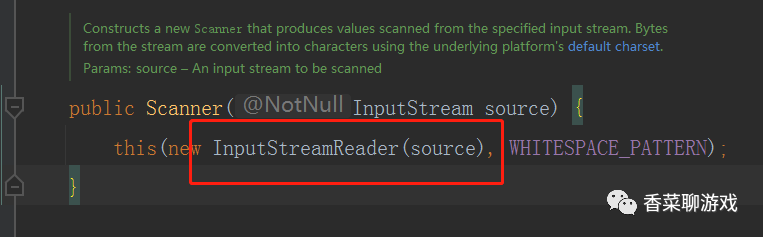
讓我們看下源碼是啥情況:
到此這篇關(guān)于你肯定能看懂的Java IO相關(guān)知識總結(jié)的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java IO內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. android 控件同時監(jiān)聽單擊和雙擊實例2. Python 忽略文件名編碼的方法3. 解決vue頁面刷新,數(shù)據(jù)丟失的問題4. vue路由分文件拆分管理詳解5. python Selenium 庫的使用技巧6. vue+vuex+axios從后臺獲取數(shù)據(jù)存入vuex,組件之間共享數(shù)據(jù)操作7. python logging.info在終端沒輸出的解決8. android studio實現(xiàn)簡單的計算器(無bug)9. 詳解android adb常見用法10. python 讀txt文件,按‘,’分割每行數(shù)據(jù)操作
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備