Java實(shí)現(xiàn)連連看算法
連連看是個(gè)經(jīng)典的小游戲,規(guī)則是:兩圖案相同的方塊在2折以內(nèi)的線連接下可以消除。里面的算法還是非常有趣,今天來研究一下。
初始化棋盤假設(shè)有一個(gè)8*8的棋盤,我們要將其擴(kuò)充至10*10,為什么?因?yàn)檫@樣外圍的連接就可以不用越界了。
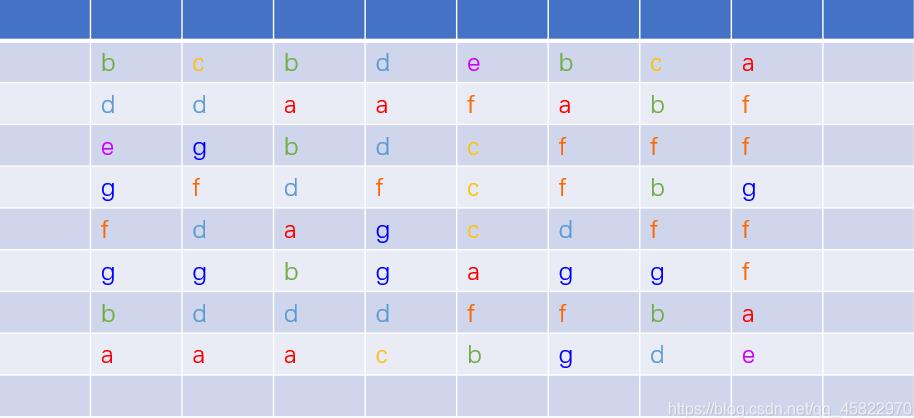
判斷是否具備消除的基本條件有 3 個(gè)
兩個(gè)方塊不能是同一個(gè)坐標(biāo) 兩個(gè)方塊必須是同種類型(圖案) 兩個(gè)方塊中不能有任何一個(gè)已經(jīng)消除過的(消除過后的值用 mark 表示)// 判斷是否具備消除的基本條件:兩個(gè)方塊不能是同一個(gè)坐標(biāo);兩個(gè)方塊必須是同種類型;兩個(gè)方塊中不能有任何一個(gè)已經(jīng)消除過的public static boolean basicCondition(Point a, Point b) { return !a.equals(b) && board[a.x][a.y] == board[b.x][b.y] && !isNull(a) && !isNull(b);}// 判斷格子是否為空或已經(jīng)被消除public static boolean isNull(Point c) { return board[c.x][c.y] == 0 || board[c.x][c.y] == mark;}0折消除
能0折消除,說明兩個(gè)方塊一定在同一直線上;它們可能是同一水平直線,也可能是同一垂直直線

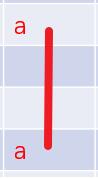
如果兩個(gè)方塊的相對(duì)位置滿足其中之一,并且我們?cè)偃ヅ袛噙B線經(jīng)過的方塊是否為空就行了。
// 判斷同一直線能否相連public static boolean matchLine(Point a, Point b) { // 水平 if (a.x == b.x) {int minY = Math.min(a.y, b.y), maxY = Math.max(a.y, b.y);for (int i = minY + 1; i < maxY; i++) { if (!isNull(new Point(a.x, i))) return false;}return true; } // 垂直 else if (a.y == b.y) {int minX = Math.min(a.x, b.x), maxX = Math.max(a.x, b.x);for (int i = minX + 1; i < maxX; i++) { if (!isNull(new Point(i, a.y))) return false;}return true; } // 不在水平或垂直上 return false;}1折消除
1折消除也就2種情況,就是上折和下折,這樣可以知道折點(diǎn)是(a.x, b.y)和(b.x, a.y) ;即判斷a點(diǎn)到折點(diǎn)能否0折消除,且b點(diǎn)到折點(diǎn)能否0折消除,且折點(diǎn)處為空
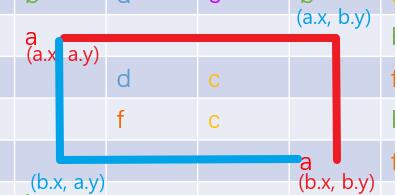
// 判斷 1 折能否相連:拐角點(diǎn) c1 和 c2 與 a b 點(diǎn)能相連并且拐角點(diǎn)為空public static boolean matchOneTurn(Point a, Point b) { Point c1 = new Point(a.x, b.y); Point c2 = new Point(b.x, a.y); return matchLine(a, c1) && matchLine(b, c1) && isNull(c1) || matchLine(a, c2) && matchLine(b, c2) && isNull(c2);}2折消除
2折消除的邏輯稍微麻煩了一點(diǎn)點(diǎn),即掃描 a 點(diǎn)所在的行和列,找一點(diǎn) c ,使得 a 與 c 能夠0折消除且 b 與 c 能1折消除;掃描 b 點(diǎn)所在的行和列,找一點(diǎn) c ,使得 b 與 c 能夠0折消除且 a 與 c 能1折消除,當(dāng)然,c 點(diǎn)不能與 a b 點(diǎn)重合,也必須為空。
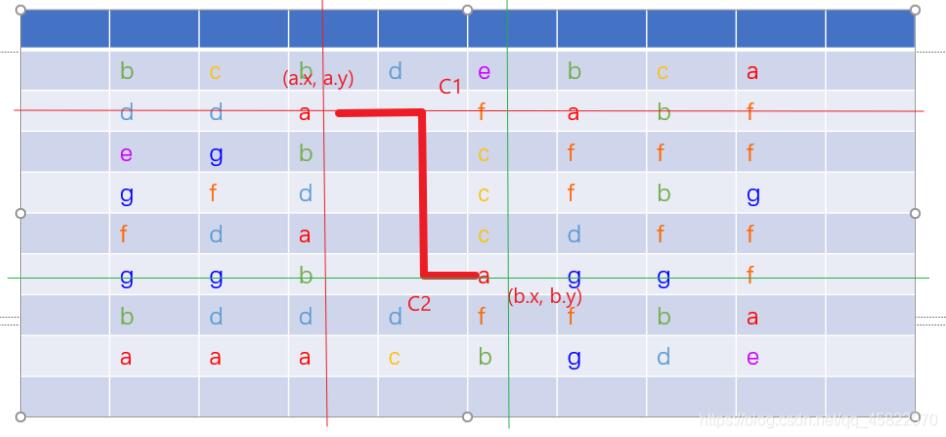
// 判斷 2 折能否相連:掃描 a 所在的行和列,找一點(diǎn) c 使之與 a 直線匹配,與 b 1 折匹配;掃描 b 所在的行和列,找一點(diǎn) c 使之與 b 直線匹配,與 a 1 折匹配public static boolean matchTwoTurn(Point a, Point b) { // 掃描 a b 所在的行 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {Point c1 = new Point(a.x, i);Point c2 = new Point(b.x, i);if (i != a.y && matchLine(c1, a) && matchOneTurn(c1, b) && isNull(c1)|| i != b.y && matchLine(c2, b) && matchOneTurn(c2, a) && isNull(c2)) return true; } // 掃描 a b 所在的列 for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {Point c1 = new Point(i, a.y);Point c2 = new Point(i, b.y);if (i != a.x && matchLine(c1, a) && matchOneTurn(c1, b) && isNull(c1)|| i != b.x && matchLine(c2, b) && matchOneTurn(c2, a) && isNull(c2)) return true; } // 不存在這樣的 c 點(diǎn) return false;}
將上述所有判斷整合,就完成了一對(duì)方塊完整的消除判斷
// 整合判斷public static boolean match(Point a, Point b) { return basicCondition(a, b) && (matchLine(a, b) || matchOneTurn(a, b) || matchTwoTurn(a, b));}
關(guān)鍵算法解決了,相信寫一個(gè)連連看游戲的障礙被打破了,是不是躍躍欲試了呢?
以上就是本文的全部?jī)?nèi)容,希望對(duì)大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。
相關(guān)文章:
1. android 控件同時(shí)監(jiān)聽單擊和雙擊實(shí)例2. 解決vue頁(yè)面刷新,數(shù)據(jù)丟失的問題3. Python 忽略文件名編碼的方法4. vue路由分文件拆分管理詳解5. 詳解android adb常見用法6. vue+vuex+axios從后臺(tái)獲取數(shù)據(jù)存入vuex,組件之間共享數(shù)據(jù)操作7. python logging.info在終端沒輸出的解決8. android studio實(shí)現(xiàn)簡(jiǎn)單的計(jì)算器(無bug)9. python Selenium 庫(kù)的使用技巧10. python 讀txt文件,按‘,’分割每行數(shù)據(jù)操作
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備